Social Security Retirement Ages Explained for Every Generation
Understanding when you can claim Social Security benefits without penalties is one of the most important financial moves toward a secure retirement. The social security retirement age chart is a roadmap that shows at what age Americans can receive full benefits, early benefits, or even larger checks by waiting. With recent updates affecting millions of workers and retirees, knowing your retirement age can help you plan smarter for the years ahead with confidence.
If you’re planning retirement or helping someone close to you make decisions about Social Security, this detailed guide will help you interpret the latest retirement age rules, understand how benefits change year by year, and see how age affects your benefit amounts with clarity and simplicity.
Start planning with peace of mind—because knowing your age in the Social Security retirement age chart is your first step toward retirement security.
(Here’s a key action you can take right now: check your birth year against the official Social Security retirement age chart to know your full benefit eligibility.)
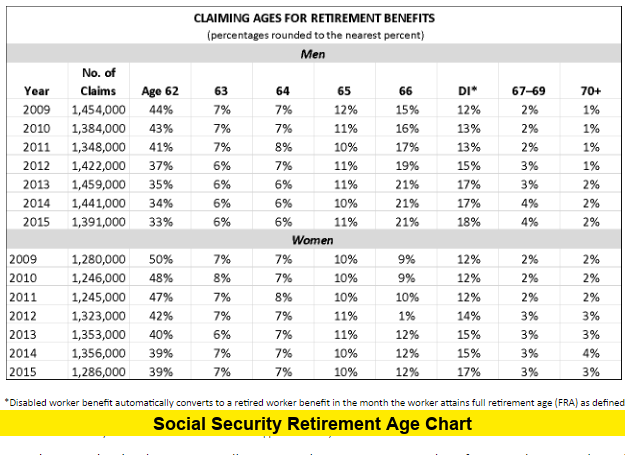
What Is the Social Security Retirement Age Chart?
The Social Security retirement age chart is an official schedule that links your year of birth to your full retirement age (FRA) — the age at which you can claim 100% of your retirement benefit amount under Social Security rules.
Here’s how it works:
- You can begin receiving Social Security retirement benefits as early as age 62, but taking benefits before your full retirement age means permanently lower monthly checks.
- If you wait beyond your FRA — up to age 70 — you may receive higher monthly benefits thanks to delayed retirement credits.
- Your exact FRA depends on the year you were born and is outlined in the retirement age chart.
The chart helps you see exactly which ages apply to your situation so you can make informed retirement decisions.
How the Full Retirement Age Has Changed Over Time
The Social Security full retirement age has risen gradually over several decades in response to longer life expectancies and economic shifts. Key points from the updated chart include:
- Born before 1938: Full retirement age was 65.
- Born 1938–1942: FRA increases gradually from 65 and 2 months up to 65 and 10 months.
- Born 1943–1954: FRA is 66.
- Born 1955–1959: FRA increases incrementally from 66 and 2 months to 66 and 10 months.
- **Born in 1960 or later: FRA is 67 — currently the standard for most working-age adults today.
This schedule reflects a long-term shift aiming to balance retirement security with the financial realities of an aging population.
Early Retirement Age vs. Full Retirement Age
In the United States, the earliest you can claim Social Security retirement benefits is age 62. This is often referred to as the early retirement age. While accessible, claiming at 62 can reduce your monthly benefit significantly — sometimes by up to 30% compared to claiming at your full retirement age.
This reduction is permanent. That means even after you reach your full retirement age, your monthly benefit stays at that reduced level if you claimed early.
On the flip side, waiting beyond your FRA — up to age 70 — will increase your monthly benefit because the system rewards delayed claiming with higher monthly checks for each year you wait.
Understanding where your age fits on the retirement age chart can help you determine whether early claiming, full retirement age claiming, or delayed claiming suits your financial goals.
Why Waiting Can Pay Off
Delaying Social Security beyond your full retirement age can increase your monthly benefit by about 8% per year up to age 70. This increase — known as delayed retirement credits — can make a big difference in your lifetime benefits, especially if you expect to live well into your 80s or beyond.
For example, someone with an FRA of 67 who waits until age 70 to claim could receive monthly checks that are substantially higher than what they would get at age 62 or 66. These increases are automatic and built into the Social Security retirement age chart and rules.
This strategy is not right for everyone, especially if health issues or urgent financial needs make early claiming necessary. Still, the retirement age chart clearly shows the potential gains from waiting if your situation allows.
How Your Benefit Amount Changes With Age
Your monthly Social Security payment depends on the age you choose to start benefits:
- At age 62: Your benefit amount can be up to 30% lower than if you wait for your full retirement age.
- At full retirement age: You receive 100% of your calculated benefit.
- After full retirement age: Your benefit rises through delayed retirement credits until age 70.
These differences make the retirement age chart more than just a table — it’s a financial planning tool that directly affects your monthly income for life.
Medicare and Retirement Age
Medicare eligibility begins at age 65, which is separate from Social Security retirement age rules. Even if your full retirement age is 67, Medicare coverage starts at 65, so planning around both systems can help you align healthcare with retirement income.
Understanding how Medicare eligibility and the Social Security retirement age chart intersect is valuable, particularly if you retire in your early 60s and need transitional healthcare coverage.
Important Planning Considerations
Here are a few practical tips when using the Social Security retirement age chart:
- Review your work history: Your lifetime earnings record affects your benefit amount.
- Check family status: Spousal and survivor benefits may change timing and benefit amounts.
- Account for taxes: Depending on your income, a portion of Social Security can be taxable.
- Track legislation changes: Benefit formulas and retirement ages can be adjusted by future policies.
Staying informed about how your year of birth aligns with retirement ages can help you make smarter decisions.
Key Takeaways from the Retirement Age Chart
- The social security retirement age chart connects birth years with specific ages for full benefits.
- You can claim Social Security as early as 62 but with reduced payments.
- Most people born in 1960 or later have a full retirement age of 67.
- Waiting to claim benefits — up to age 70 — can increase your monthly income.
- Understanding your position on the chart is essential for effective financial planning.
We’d love to hear your thoughts — share your retirement plans or questions in the comments!