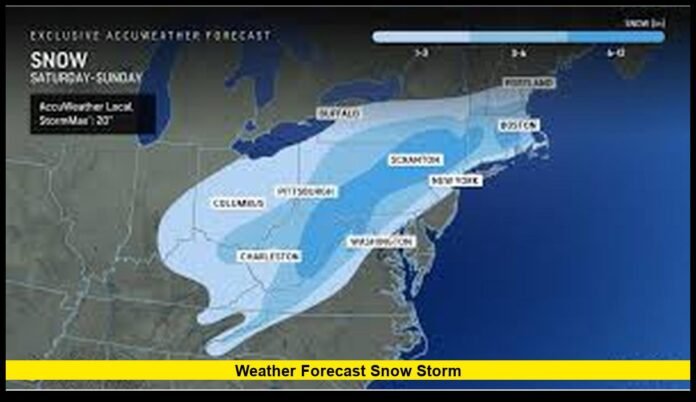
The weather forecast snow storm continues to impact millions across the United States on February 6, 2026, as fresh snowfall, strong winds, and persistent Arctic air shape conditions from the Great Lakes to the Northeast. Winter alerts remain active in multiple states, and forecasters are tracking additional systems that could bring more snow in the coming days.
Cold air has settled over much of the eastern half of the country. Several regions are experiencing below-average temperatures, while snowfall continues in parts of the Northeast and downwind of the Great Lakes. Roads remain slick in areas where snow fell earlier this week, and overnight refreezing has created icy patches for morning commuters.
Active Snow Zones Across the Northeast
Snow continues to fall across sections of New York, Pennsylvania, northern New England, and parts of the Mid-Atlantic. Accumulations vary widely depending on elevation and storm track. Some communities are seeing light coatings, while others report several inches.
Wind gusts are increasing the impact. Blowing snow has reduced visibility in open areas and along major highways. Drivers in rural and suburban zones face drifting snow in exposed stretches of road.
Lake-enhanced snow remains a major factor near the Great Lakes. Cold air moving across relatively warmer lake waters has triggered narrow but intense snow bands. These bands can quickly produce heavy snowfall in localized areas. Just a few miles can separate minor flurries from several inches of accumulation.
Great Lakes Region: Lake-Effect Snow Intensifies
Cities downwind of Lakes Erie and Ontario are experiencing periodic bursts of heavy snow. Wind direction plays a critical role in determining where the heaviest totals land. Communities in western and central New York have reported rapidly changing conditions as snow bands shift.
Local transportation departments are operating around the clock. Plows are clearing highways and secondary roads, yet snowfall rates occasionally outpace removal efforts. Drivers are urged to reduce speed and maintain safe distances between vehicles.
Air temperatures remain below freezing across the region. Combined with wind, the cold is increasing the risk of frostbite during extended outdoor exposure.
Mid-Atlantic: Cold Air Follows Light Snow
Northern portions of the Mid-Atlantic are seeing light snowfall, especially in elevated terrain. Even where snow totals remain modest, the sharp temperature drop behind the system is drawing attention.
Wind chills have fallen into the single digits in some inland communities. Overnight lows are dipping well below freezing, allowing snow and slush to harden into ice.
Urban centers are treating roads and sidewalks, but untreated surfaces remain hazardous. Pedestrians should use caution when navigating steps, parking lots, and shaded sidewalks.
Southeast: Lingering Effects from Earlier Winter Activity
Parts of the Southeast experienced unusual winter weather in late January, including measurable snowfall in areas that rarely see accumulation. While current snow is not widespread in the region, cold air continues to dominate morning temperatures.
Some inland sections are starting the day with frost and icy patches on bridges and overpasses. Residents unaccustomed to winter driving conditions are advised to remain cautious during early commutes.
Arctic Air Mass Holds Strong
A persistent Arctic air mass remains anchored over much of the eastern United States. This air mass is reinforcing snow potential while prolonging icy conditions even after precipitation ends.
Daytime highs in several northern states are struggling to climb above freezing. Overnight lows are falling into the teens and single digits in colder locations. Wind gusts amplify the chill, creating conditions that feel significantly colder than the actual air temperature.
Extended cold spells increase stress on infrastructure. Heating systems are running continuously, and energy demand remains elevated in many regions. Residents should ensure furnaces and space heaters operate safely and that vents remain clear of snow.
Travel Disruptions Continue
Winter weather is affecting both ground and air travel.
Major highways in the Northeast and Great Lakes regions are experiencing slower traffic due to reduced visibility and slick surfaces. Law enforcement agencies report spinouts and minor accidents during peak snowfall periods.
Airports in snow-affected cities are managing de-icing operations. Delays have been reported as aircraft require treatment before departure. Travelers should check flight status prior to heading to the airport.
Public transit systems are also adjusting schedules. Snow and ice accumulation on tracks and platforms can slow service in some metropolitan areas.
Snowfall Overview by Region
While totals vary, the current weather forecast snow storm pattern is producing measurable impacts across multiple zones:
- Northeast: Light to moderate snow with localized heavier bands.
- Great Lakes: Lake-effect snow with shifting high-accumulation areas.
- Mid-Atlantic: Light snow in northern sections and colder temperatures region-wide.
- Interior New England: Continued snow showers with gusty winds.
Snowfall distribution remains uneven due to shifting storm tracks and localized banding.
Refreezing and Black Ice Concerns
As temperatures remain below freezing overnight, refreezing becomes a significant hazard. Melted snow from daytime sunshine can quickly turn into ice after sunset.
Bridges and overpasses freeze first due to air circulation above and below the structure. Drivers should approach these areas carefully, especially during early morning hours.
Black ice is particularly dangerous because it blends into pavement and may not be visible. Slower speeds and increased following distances reduce the risk of collisions.
Impact on Schools and Businesses
Several school districts in snow-affected regions have implemented delays or remote learning days. Decisions vary by county depending on road conditions and snowfall intensity.
Businesses in heavily impacted communities are adjusting operating hours. Snow removal crews continue clearing parking lots and sidewalks to maintain access.
Retail and grocery stores report increased demand for cold-weather supplies such as ice melt, batteries, and space heaters. Residents are stocking up on essentials in preparation for continued winter conditions.
Mountain West: Ongoing Snow in Higher Elevations
While the primary focus remains on the eastern half of the country, mountain regions in the West are also receiving snowfall. Pacific systems moving inland are delivering moderate accumulations at higher elevations.
Ski resorts are benefiting from fresh powder, though mountain travel can be challenging during peak snowfall periods. Drivers crossing mountain passes should monitor conditions closely.
What to Expect Over the Next Several Days
Forecast models indicate that the active winter pattern may continue through mid-February. Additional disturbances could move across the northern United States, bringing renewed snow chances to the Plains, Great Lakes, and Northeast.
Temperatures are expected to remain below average in many eastern states for several more days. This prolonged cold ensures that existing snow cover will not melt quickly.
Residents should remain attentive to updated alerts and short-term forecast changes. Snow bands, especially near the Great Lakes, can shift with little notice.
Winter Safety Reminders
Communities facing ongoing snow and cold should follow these safety steps:
- Dress in insulated layers and cover exposed skin.
- Keep vehicles stocked with blankets and emergency supplies.
- Allow extra time for travel and avoid sudden braking.
- Clear snow from roofs and vents to prevent buildup.
- Check on elderly or vulnerable neighbors during extreme cold.
Simple precautions reduce the risk of cold-related injuries and accidents.
Why This Pattern Matters
The current weather forecast snow storm setup highlights how persistent Arctic air can maintain winter hazards even without a single major blizzard. Successive smaller systems can create cumulative impacts through repeated snowfall and sustained cold.
Snow accumulation affects transportation, commerce, and daily routines. Extended freezing temperatures compound the challenge by preventing rapid melting.
Communities across the northern United States remain in winter mode, with plows, salt crews, and emergency responders working continuously to maintain safety.
The coming days will determine how much additional snow falls and whether cold air begins to moderate. Until then, winter conditions remain firmly in place across broad sections of the country.
Winter weather continues to evolve, so stay informed, watch local conditions closely, and share how snow and cold are affecting your area.