The diagnosis of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) has evolved rapidly, with advances in genetic testing and diagnostic imaging improving accuracy and speed. As of October 2025, new tools and insights are transforming how U.S. clinicians identify and confirm cases of this complex inherited neuropathy.
What Is CMT and Why Diagnosis Matters
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) is a group of hereditary neurological disorders that affect the peripheral nerves — those outside the brain and spinal cord. These nerves control muscle movement and transmit sensory information between the limbs and the brain.
CMT typically causes symptoms such as:
- Foot deformities like high arches or hammertoes
- Muscle weakness in the lower legs and feet
- Numbness or loss of sensation in the hands and feet
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
Early diagnosis matters because it helps patients and families understand the subtype of the disease, plan for future care, and gain access to supportive therapies and clinical trials. Early intervention with physical therapy, orthotics, or mobility support can significantly improve quality of life.
How the Diagnosis Process Works Today
Diagnosing Charcot Marie Tooth disease involves several key steps that help doctors confirm the condition and determine its subtype:
- Medical and Family History
A neurologist begins by reviewing a patient’s symptoms, age of onset, and any family history of neuropathy. Because CMT is genetic, identifying affected relatives can be a critical clue. - Neurologic Examination
Physical exams assess muscle strength, reflexes, balance, and sensation in the hands and feet. Common findings include weakness in the lower limbs, reduced reflexes, and characteristic foot deformities. - Electrodiagnostic Testing
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) measure how quickly electrical signals move through nerves and muscles. These tests can determine whether the problem lies in the nerve fibers (axons) or their protective covering (myelin). - Genetic Testing
The most significant advancement in recent years, genetic testing identifies the exact mutation responsible for CMT. Today’s panels can detect changes in more than 130 genes associated with over 160 distinct forms of the disease. - Imaging and Biopsy (if necessary)
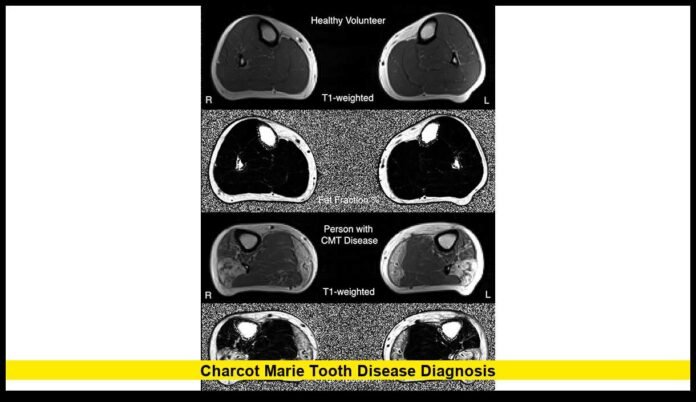
MRI scans or nerve biopsies are occasionally used when results are unclear or to exclude other conditions that mimic CMT.
Key Updates in Diagnosis for 2025
In 2025, several major updates have shaped how CMT diagnosis is handled in the U.S.:
- Expanded Genetic Database: Researchers have identified more than 130 genes linked to various subtypes of CMT, with classifications refined to reflect genetic rather than purely clinical distinctions.
- Subtype Reclassification: The traditional labels (CMT1, CMT2, etc.) are being updated as many subtypes overlap genetically. Modern diagnosis relies more on gene-based identification.
- Precision Testing: Next-generation sequencing has become faster and more affordable, allowing broader access to detailed genetic testing.
- Emerging Biomarkers: Studies using advanced MRI techniques and wearable digital devices are helping track disease progression, providing additional tools for diagnosis and monitoring.
- Clinical Trial Readiness: Precise genetic diagnosis now determines eligibility for many gene-specific clinical trials, underscoring the value of early and accurate testing.
Why Genetic Testing Is Now Essential
Genetic testing has shifted from optional to standard practice in most suspected CMT cases. This change is driven by its ability to provide clarity, improve care, and connect patients with potential therapies.
Benefits of genetic testing include:
- Accurate diagnosis: Confirms the presence and type of CMT.
- Predictive insight: Helps understand how the disease might progress.
- Clinical relevance: Determines eligibility for targeted treatments and research studies.
- Family planning: Reveals inheritance patterns (dominant, recessive, or X-linked) and helps relatives understand their risks.
Because many subtypes overlap clinically, genetic confirmation is now seen as the gold standard for diagnosis.
Challenges and Considerations in Diagnosis
Despite the progress, several challenges remain for both patients and clinicians:
- Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUS): Genetic tests sometimes detect mutations whose effects are unclear, making diagnosis complex.
- Overlap with Other Neuropathies: Conditions such as diabetic or toxic neuropathies can mimic CMT symptoms and complicate the diagnostic process.
- Access and Cost: Comprehensive genetic testing and neuromuscular specialists may not be available in all areas or fully covered by insurance.
- Communication Gap: The evolving classification system can be confusing for patients and healthcare providers unfamiliar with the new gene-based terminology.
While these challenges exist, they are gradually being addressed through improved awareness, broader testing access, and ongoing education among clinicians.
Practical Steps for Patients Suspected of Having CMT
If you suspect you or a loved one may have Charcot Marie Tooth disease, here are practical steps to take:
- Consult a neurologist experienced in neuromuscular disorders.
- Ask about nerve conduction and EMG studies to evaluate nerve and muscle function.
- Request genetic testing to identify the specific mutation involved.
- Gather family medical history to help doctors identify potential inheritance patterns.
- Explore supportive care early, including physical or occupational therapy, orthotics, and mobility aids.
- Stay informed about ongoing clinical trials and registries, which may offer diagnostic and treatment opportunities.
These proactive steps ensure faster and more accurate identification, opening the door to emerging therapies as research continues to advance.
What an Accurate Diagnosis Enables for the Future
A precise Charcot Marie Tooth disease diagnosis does more than put a name to symptoms — it lays the foundation for progress. Once the genetic subtype is confirmed, patients can:
- Join clinical research programs exploring gene therapy and targeted treatments.
- Receive personalized medical care tailored to their specific subtype.
- Plan proactively for long-term support, mobility options, and symptom management.
- Connect with community resources that provide education, advocacy, and emotional support.
As genetic knowledge deepens and new technologies emerge, accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of better care, improved management, and eventual cures.
In summary, the approach to Charcot Marie Tooth disease diagnosis in 2025 reflects major progress in precision medicine. With expanded genetic panels, advanced imaging, and rising awareness, patients in the U.S. are achieving faster, more accurate diagnoses than ever before. Though no definitive cure yet exists, these diagnostic breakthroughs are building the foundation for the next generation of CMT treatments.
Have you or someone you know been recently diagnosed with CMT? Share your thoughts and experiences below — your story could help others stay informed.