A New Health Concern Emerges
In a groundbreaking discovery, health experts have identified the first known U.S. case of a sexually transmitted fungal infection. This new form of ringworm was detected in a man from New York City, marking a significant moment in the study of sexually transmitted infections.
The Discovery
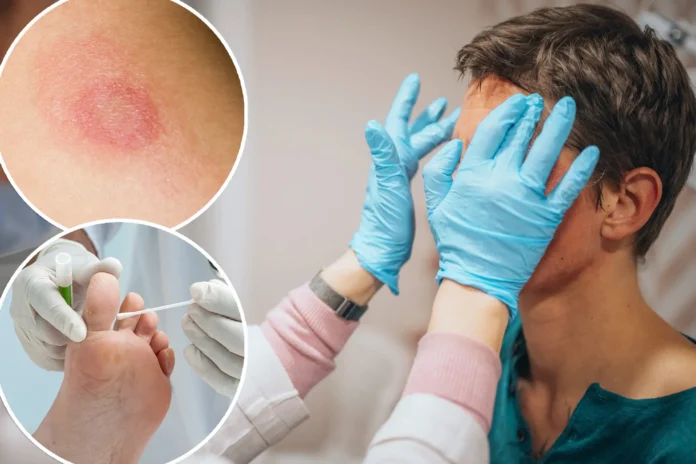
The case was detailed in a study published in JAMA Dermatology. The infected individual, a man in his 30s, had traveled to England, Greece, and California before returning to New York City, where he developed tinea—a type of skin rash—on his penis, buttocks, and limbs. This case underscores the global nature of infectious diseases and the importance of vigilant healthcare practices.
The Nature of the Infection
The fungal infection, caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII (TMVII), is highly contagious and can persist for months even with treatment. Unlike typical ringworm, which forms neat circles, this new strain can present as lesions that might be mistaken for eczema, delaying appropriate treatment.
Symptoms and Spread
This new ringworm causes tinea, which can spread to the face, limbs, groin, and feet. The New York man’s infection is particularly notable as he reported multiple male sexual partners during his travels, none of whom had similar symptoms. This highlights the potential for asymptomatic carriers and the importance of awareness and preventive measures.
Expert Insights
Dr. Avrom Caplan, the study’s lead author and assistant professor of dermatology at NYU’s Grossman School of Medicine, emphasized the need for increased awareness among healthcare providers. Dr. John Zampella, another study author, highlighted the importance of directly asking patients about rashes in the groin and buttocks, especially those who are sexually active and have recently traveled.
Addressing Stigma
Caplan acknowledged the potential for stigma and anxiety, particularly given recent public focus on similar demographics during the mpox outbreak. However, he stressed that this infection is very different from mpox, which is a viral infection previously known as monkeypox.
Treatment and Challenges
Currently, TMVII infections seem to respond to standard treatments, such as terbinafine, an oral antifungal medication. However, Caplan warned of another fungal infection, Trichophyton indotinea, which is resistant to terbinafine. This strain, widespread in India and now reported globally, poses a greater challenge for treatment.
Importance of Awareness
The main aim of reporting this case is to raise awareness among clinicians and the public. Dermatophytes like TMVII can cause significant and inflammatory infections, and it’s crucial for healthcare providers to consider this in their diagnoses. For patients, it’s a reminder to seek medical advice if they have persistent, painful, itchy, or inflamed lesions in the genital area.
Moving Forward
As health experts continue to monitor and study this new fungal infection, the key message is vigilance and awareness. Both healthcare providers and patients must be informed and proactive in addressing potential symptoms and seeking timely treatment.
Stay tuned for more updates on this developing story and other health news. For now, it’s essential to remain informed and cautious, especially when traveling and engaging in activities that may increase the risk of infection.
See Also- Shark Attack Double Incident in Walton County, Florida